TM1637 LED Display ansteuern - Only 4 PIN Red Common Anode 4-Segment Digital Tube Display For Arduino Raspberry: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Aus www.electronic-man.randschtoischlotzer.de
Eman (Diskussion | Beiträge) (→Anschlußschema am BananaPiPro) |
Eman (Diskussion | Beiträge) (→Anschlußschema am BananaPiPro) |
||
| Zeile 25: | Zeile 25: | ||
::*GPIO 23 auf GPIO 20 (RPi-Pin 16 auf 38) | ::*GPIO 23 auf GPIO 20 (RPi-Pin 16 auf 38) | ||
::*GPIO 24 auf GPIO 21 (RPi-Pin 18 auf 40) | ::*GPIO 24 auf GPIO 21 (RPi-Pin 18 auf 40) | ||
| + | nano 47digitclock.py | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
Aktuelle Version vom 28. Januar 2018, 15:24 Uhr
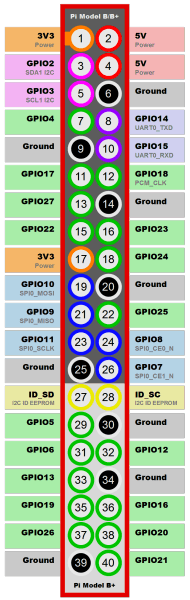
Anschlußschema am BananaPiPro
| TM1637 Board Pin | Funktion | RPi PIN | RPi Funktion |
|---|---|---|---|
| GND | Ground | 39 | GND |
| VCC | +3,3V Power | 1 | 3,3V |
| DIO | Data In | 38 | GPIO 20 |
| CLK | Clock | 40 | GPIO 21 |
- Python Scripte:
- downloaden:
wget https://raspberrytips.nl/files/tm1637.py wget https://raspberrytips.nl/files/47digitclock.py
-
4747digitclock.pyfür obige Schaltung anpassen:
- GPIO 23 auf GPIO 20 (RPi-Pin 16 auf 38)
- GPIO 24 auf GPIO 21 (RPi-Pin 18 auf 40)
-
nano 47digitclock.py
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # https://raspberrytips.nl/tm1637-4-digit-led-display-raspberry-pi/ import sys import time import datetime import RPi.GPIO as GPIO import tm1637 #CLK -> GPIO20 (Pin 38) #DI0 -> GPIO21 (Pin 40) Display = tm1637.TM1637(20,21,tm1637.BRIGHT_TYPICAL) Display.Clear() Display.SetBrightnes(1) while(True): now = datetime.datetime.now() hour = now.hour minute = now.minute second = now.second currenttime = [ int(hour / 10), hour % 10, int(minute / 10), minute % 10 ] Display.Show(currenttime) Display.ShowDoublepoint(second % 2) time.sleep(1)
- ausführbar machen:
chmod +x *.py
- um automatisch beim Booten zu starten, die Cron-Job-Tabelle um einen Mount-Befehl erweitern:
crontab -e
# Edit this file to introduce tasks to be run by cron. # # Each task to run has to be defined through a single line # indicating with different fields when the task will be run # and what command to run for the task # # To define the time you can provide concrete values for # minute (m), hour (h), day of month (dom), month (mon), # and day of week (dow) or use '*' in these fields (for 'any').# # Notice that tasks will be started based on the cron's system # daemon's notion of time and timezones. # # Output of the crontab jobs (including errors) is sent through # email to the user the crontab file belongs to (unless redirected). # # For example, you can run a backup of all your user accounts # at 5 a.m every week with: # 0 5 * * 1 tar -zcf /var/backups/home.tgz /home/ # # For more information see the manual pages of crontab(5) and cron(8) # # m h dom mon dow command @reboot /root/47digitclock.py &
- Zeile einfügen:
@reboot /root/47digitclock.py &
- im obigen Script verwendete Klasse:
tm1637.py
- im obigen Script verwendete Klasse:
# https://raspberrytips.nl/tm1637-4-digit-led-display-raspberry-pi/ import sys import os import time import RPi.GPIO as IO IO.setwarnings(False) IO.setmode(IO.BCM) HexDigits = [0x3f,0x06,0x5b,0x4f,0x66,0x6d,0x7d,0x07,0x7f,0x6f,0x77,0x7c,0x39,0x5e,0x79,0x71] ADDR_AUTO = 0x40 ADDR_FIXED = 0x44 STARTADDR = 0xC0 BRIGHT_DARKEST = 0 BRIGHT_TYPICAL = 2 BRIGHT_HIGHEST = 7 OUTPUT = IO.OUT INPUT = IO.IN LOW = IO.LOW HIGH = IO.HIGH class TM1637: __doublePoint = False __Clkpin = 0 __Datapin = 0 __brightnes = BRIGHT_TYPICAL; __currentData = [0,0,0,0]; def __init__( self, pinClock, pinData, brightnes ): self.__Clkpin = pinClock self.__Datapin = pinData self.__brightnes = brightnes; IO.setup(self.__Clkpin,OUTPUT) IO.setup(self.__Datapin,OUTPUT) # end __init__ def Clear(self): b = self.__brightnes; point = self.__doublePoint; self.__brightnes = 0; self.__doublePoint = False; data = [0x7F,0x7F,0x7F,0x7F]; self.Show(data); self.__brightnes = b; # restore saved brightnes self.__doublePoint = point; # end Clear def ShowInt(self, i): s = str(i) self.Clear() for i in range(0,len(s)): self.Show1(i, int(s[i])) def Show( self, data ): for i in range(0,4): self.__currentData[i] = data[i]; self.start(); self.writeByte(ADDR_AUTO); self.stop(); self.start(); self.writeByte(STARTADDR); for i in range(0,4): self.writeByte(self.coding(data[i])); self.stop(); self.start(); self.writeByte(0x88 + self.__brightnes); self.stop(); # end Show def SetBrightnes(self, brightnes): # brightnes 0...7 if( brightnes > 7 ): brightnes = 7; elif( brightnes < 0 ): brightnes = 0; if( self.__brightnes != brightnes): self.__brightnes = brightnes; self.Show(self.__currentData); # end if # end SetBrightnes def ShowDoublepoint(self, on): # shows or hides the doublepoint if( self.__doublePoint != on): self.__doublePoint = on; self.Show(self.__currentData); # end if # end ShowDoublepoint def writeByte( self, data ): for i in range(0,8): IO.output( self.__Clkpin, LOW) if(data & 0x01): IO.output( self.__Datapin, HIGH) else: IO.output( self.__Datapin, LOW) data = data >> 1 IO.output( self.__Clkpin, HIGH) #endfor # wait for ACK IO.output( self.__Clkpin, LOW) IO.output( self.__Datapin, HIGH) IO.output( self.__Clkpin, HIGH) IO.setup(self.__Datapin, INPUT) while(IO.input(self.__Datapin)): time.sleep(0.001) if( IO.input(self.__Datapin)): IO.setup(self.__Datapin, OUTPUT) IO.output( self.__Datapin, LOW) IO.setup(self.__Datapin, INPUT) #endif # endwhile IO.setup(self.__Datapin, OUTPUT) # end writeByte def start(self): IO.output( self.__Clkpin, HIGH) # send start signal to TM1637 IO.output( self.__Datapin, HIGH) IO.output( self.__Datapin, LOW) IO.output( self.__Clkpin, LOW) # end start def stop(self): IO.output( self.__Clkpin, LOW) IO.output( self.__Datapin, LOW) IO.output( self.__Clkpin, HIGH) IO.output( self.__Datapin, HIGH) # end stop def coding(self, data): if( self.__doublePoint ): pointData = 0x80 else: pointData = 0; if(data == 0x7F): data = 0 else: data = HexDigits[data] + pointData; return data # end coding # end class TM1637